Leading-Edge Surgical Techniques Allow Patients to Breathe Better
Breathing is a basic life function. For individuals experiencing breathing difficulties due to congenital defects, external injury or medical procedures, such…

Update your location to show providers, locations, and services closest to you.
Blockage of the upper airway occurs when the upper breathing passages become narrowed or blocked, making it hard to breathe. Areas in the upper airway that can be affected are the windpipe (trachea), voice box (larynx), or throat (pharynx).
Airway obstruction - acute upper
The airway can become narrowed or blocked due to many causes, including:
People at higher risk for airway obstruction include those who have:
Young children and older adults are also at higher risk for airway obstruction.
Symptoms vary, depending on the cause. But some symptoms are common to all types of airway blockage. These include:
The health care provider will do a physical examination and check the airway. The provider will also ask about the possible cause of the blockage.
Tests are usually not necessary, but may include:
Treatment depends on the cause of the blockage.
If the obstruction is due to a foreign body, such as a piece of food that has been breathed in, doing abdominal thrusts, back blows, or chest compressions can save the person's life.
Prompt treatment is often successful. But the condition is dangerous and may be fatal, even when treated.
If the obstruction is not relieved, it can cause:
Airway obstruction is often an emergency. Call 911 or the local emergency number for medical help. Follow instructions on how to help keep the person breathing until help arrives.
Prevention depends on the cause of the upper airway obstruction.
The following methods may help prevent an obstruction:
Learn to recognize the universal sign for inability to breathe due to a blocked airway: grabbing the neck with one or both hands. Also learn how to clear a foreign body from the airway using a method such as abdominal thrusts.
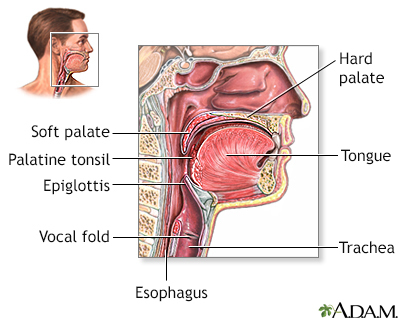

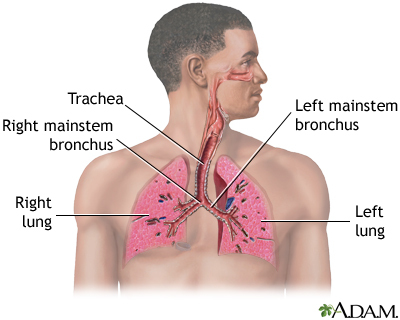
Driver BE, Reardon RF. Basic airway management and decision making. In: Roberts JR, Custalow CB, Thomsen TW, eds. Roberts and Hedges' Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 3.
Rose E. Pediatric respiratory emergencies: upper airway obstruction and infections. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 167.
Thomas SH, Goodloe JM. Foreign bodies. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 53.

Breathing is a basic life function. For individuals experiencing breathing difficulties due to congenital defects, external injury or medical procedures, such…
