Alveolar abnormalities
Definition
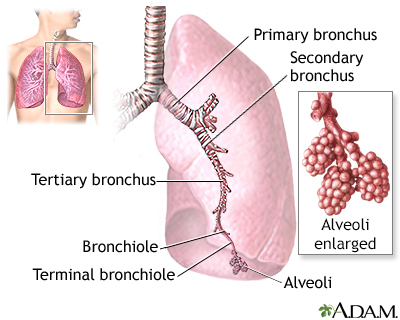
Alveolar abnormalities are changes in the tiny air sacs in the lungs, called alveoli. Alveoli allow oxygen to enter the blood. They are very thin to let oxygen move from the lungs to the blood vessels, and for carbon dioxide to be removed from the blood vessels to the lungs.
Depending on the disease, alveoli may:
- Collapse
- Fuse together
- Develop thickened linings
- Fill with fluid
- Fill with blood
- Fill with pus
- Get destroyed
Once this occurs oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange do not happen normally and lead to different disorders.
These changes can be temporary or permanent, depending on the disease.
Gallery
References
Albertine KH, Ramirez MI, Morty RE. Anatomy. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 1.
Hall JE, Hall ME. Respiratory insufficiency - pathophysiology, diagnosis, oxygen therapy. In: Hall JE, Hall ME, eds. Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 43.