Apolipoprotein B100
Definition
Apolipoprotein B100 (apoB100) is a protein that plays a role in moving cholesterol around your body. It is a form of low density lipoprotein (LDL).
Mutations (changes) in the gene that directs the body's production of apoB100 can cause a condition called familial hypercholesterolemia. This is a form of high blood cholesterol that is passed down in families (inherited).
This article discusses the test used to measure the level of apoB100 in the blood.
Patient Education Video: Cholesterol and triglyceride test
Alternative Names
ApoB100; Apoprotein B100; Hypercholesterolemia - apolipoprotein B100
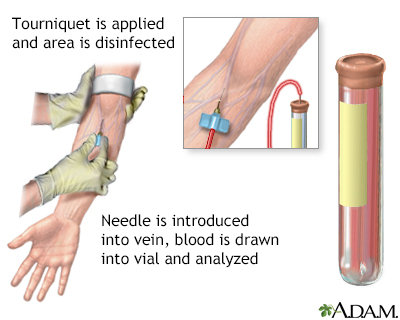
How the Test is Performed
How to Prepare for the Test
Your health care provider may tell you not to eat or drink anything for 4 to 6 hours before the test.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, you may feel moderate pain, or only a prick or stinging sensation. Afterward, there may be some throbbing.
Why the Test is Performed
Most often, this test is done to help determine the cause or specific type of high blood cholesterol. It is not clear whether the information helps improve treatment. Because of this, most health insurance companies do not pay for the test. If you do not have a diagnosis of high cholesterol or heart disease, this test may not be recommended for you.
Normal Results
The normal range is about 50 to 150 mg/dL.
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some laboratories use different measurements or may test different specimens. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An abnormal result may mean you have high lipid (fat) levels in your blood. A medical term for this is hyperlipidemia.
Other disorders that may be associated with high apoB100 levels include atherosclerotic vascular disease such as angina pectoris (chest pain that occurs with activity or stress) and heart attack.
Risks
Risks linked with having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Hematoma (blood buildup under the skin)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
- Multiple punctures to locate veins
Considerations
Apolipoprotein measurements may provide more detail about your risk for heart disease, but the added value of this test beyond a lipid panel is unknown.
Gallery

References
Fazio S, Linton MF. Regulation and clearance of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins. In: Ballantyne CM, ed. Clinical Lipidology: A Companion to Braunwald's Heart Disease. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2015:chap 2.
Genest J, Mora S, Libby P. Lipoprotein disorders and cardiovascular disease. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 27.
Libby P. The vascular biology of atherosclerosis. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 24.
Meeusen JW, Ueda M, Nordestgaard BG, Remaley AT. Lipids and lipoproteins. In: Rifai N, Chiu RWK, Young I, Burnham C-A D, Wittwer CT, eds. Tietz Textbook of Laboratory Medicine. 7th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2023:chap 36.
Robinson JG. Disorders of lipid metabolism. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 195.