Biopsy - biliary tract
Definition
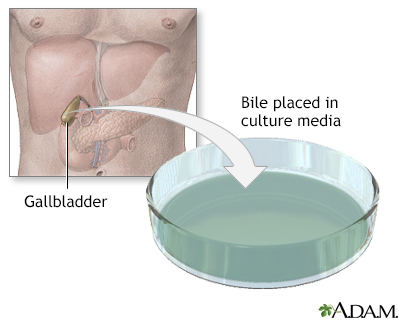
A biliary tract biopsy is the removal of small amounts of cells and fluids from the duodenum, bile ducts, pancreas, or pancreatic duct. The sample is examined under a microscope.
Alternative Names
Cytology analysis - biliary tract; Biliary tract biopsy
How the Test is Performed
A sample for a biliary tract biopsy can be obtained in different ways.
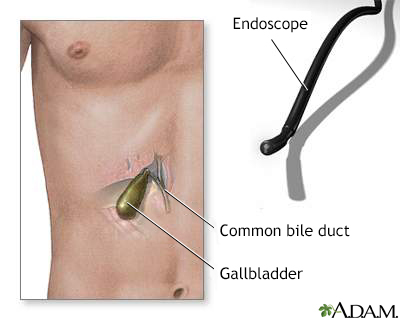
A needle biopsy can be done if you have a well-defined tumor.
- The biopsy site is cleaned.
- A thin needle is inserted into the area to be tested, and a sample of cells and fluid are removed.
- The needle is then removed.
- Pressure is put on the area to stop any bleeding. The site will be covered with a bandage.
If you have a narrowing or blockage of the bile or pancreatic ducts, a sample can be taken during procedures such as:
How to Prepare for the Test
You may not be able to eat or drink 8 to 12 hours or more before the test. Your health care provider will tell you ahead of time what you need to do.
Make sure you have someone to drive you home.
How the Test will Feel
How the test will feel depends on the type of procedure used to remove the biopsy sample. With a needle biopsy, you may feel a sting as the needle is inserted. Some people feel a cramping or pinching feeling during the procedure.
Medicines that stop pain and help you relax are commonly used for other biliary tract biopsy methods.
Why the Test is Performed
A biliary tract biopsy can determine if a tumor started in the liver or spread from another location. It also can determine if the tumor is cancerous.
This test may be done:
- After a physical exam, x-ray, MRI, CT scan, or ultrasound shows abnormal growths in your biliary tract
- To test for diseases or infection
Normal Results
A normal result means there are no signs of cancer, disease, or infection in the biopsy sample.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may be due to:
- Cancer of the bile ducts (cholangiocarcinoma)
- Cysts in the liver
- Liver cancer
- Pancreatic cancer
- Swelling and scarring of the bile ducts (primary sclerosing cholangitis)
Risks
Risks depend on how the biopsy sample was taken.
Risks may include:
- Bleeding at the biopsy site
- Infection
Gallery
References
Chernecky CC, Berger BJ. Biopsy, site-specific-specimen. In: Chernecky CC, Berger BJ, eds. Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures. 6th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders; 2013:199-201.
Gibson RN, Sutherland TR. The biliary system. In: Adam A, Dixon AK, Gillard JH, Schaefer-Prokop CM, eds. Grainger & Allison's Diagnostic Radiology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 24.
Wyatt JI, Haugk B. Liver, biliary system and pancreas. In: Cross SS, ed. Underwood's Pathology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 16.
