Go Mini Scientific Challenge
Congratulations Dr. Mattia Prosperi on winning Illumina, Inc.'s #GoMiniGrant! Dr. Prosperi will work with UF Emerging Pathogens Institute's Dr. Volker Mai to…

Update your location to show providers, locations, and services closest to you.
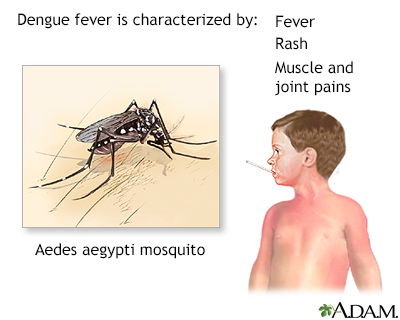
Dengue fever is a virus-caused disease that is spread by mosquitoes. Dengue in its mild form causes fever and a rash and lasts about a week. Severe dengue can cause shock, internal bleeding, and death. About 1 out of 20 people with dengue will develop severe dengue within a few hours after symptoms start. The main risk factor for severe dengue is a prior infection with dengue.
O'nyong-nyong fever; Dengue-like disease; Breakbone fever; Dengue hemorrhagic fever
Dengue fever is caused by 1 of 4 different but related viruses. It is spread by the bite of mosquitoes, most commonly the mosquito Aedes aegypti, which is found in tropic and subtropic regions. This area includes parts of:
Dengue fever is rare in the US mainland, but has been found in Hawaii, Florida, and Texas.
Dengue fever begins with a sudden high fever, often as high as 105°F (40.5°C), 4 to 7 days after the infection.
A flat, red rash may appear over most of the body 2 to 5 days after the fever starts. A second rash, which looks like the measles, appears later in the disease. Infected people may have increased skin sensitivity and are very uncomfortable.
Other symptoms include:
Symptoms of severe dengue can occur 24 to 48 hours after fever has gone away. Severe symptoms include:
If you or anyone you know has symptoms of severe dengue, call 911 or the local emergency number right away.
Tests that may be done to diagnose this condition include:
There is no specific treatment for dengue fever. Fluids are given if there are signs of dehydration. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) is used to treat a high fever.
Avoid taking aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), and naproxen (Aleve). They may increase bleeding problems.
Severe dengue is a medical emergency. It must be treated immediately at a hospital. Treatment for severe dengue is supportive and may include:
Mild cases of dengue generally last a week or more. Although uncomfortable, mild dengue fever is not deadly. People with the condition should fully recover. In some Latin American and Asian countries, severe dengue is a leading cause of death and severe illness. Early detection and treatment of severe dengue can greatly reduce the risk of death.
Untreated, dengue fever may cause the following health problems:
Contact your health care provider if you have traveled in an area where dengue fever is known to occur and you have symptoms of the disease.
Clothing, mosquito repellent, and netting can help reduce the risk for mosquito bites that can spread dengue fever and other infections. Limit outdoor activity during mosquito season, especially when they are most active, at dawn and dusk.


Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Dengue. www.cdc.gov/dengue/index.html. Updated August 3, 2022. Accessed December 8, 2022.
Endy TP. Viral febrile illnesses and emerging pathogens. In: Ryan ET, Hill DR, Solomon T, Aronson NE, Endy TP, eds. Hunter's Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 36.
Thomas SJ, Endy TP, Rothman AL, Barrett AD. Flaviviruses (dengue, yellow fever, Japanese encephalitis, West Nile encephalitis, Usutu encephalitis, St. Louis encephalitis, tick-borne encephalitis, Kyasanur forest disease, Alkhurma hemorrhagic fever, Zika). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 153.
World Health Organization website. Dengue and severe dengue. www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dengue-and-severe-dengue. Updated January 10, 2022. Accessed December 8, 2022.

Congratulations Dr. Mattia Prosperi on winning Illumina, Inc.'s #GoMiniGrant! Dr. Prosperi will work with UF Emerging Pathogens Institute's Dr. Volker Mai to…

April 2, 2015
Implementing a vaccine trial during an epidemic can be difficult, particularly in countries with poor transportation, limited vaccine supplies and difficulty…
Department of Biostatistics, +3 more
