Drug allergies
Definition
Drug allergies are a group of symptoms caused by an allergic reaction to a drug (medicine).
Alternative Names
Allergic reaction - drug (medication); Drug hypersensitivity; Medication hypersensitivity
Causes
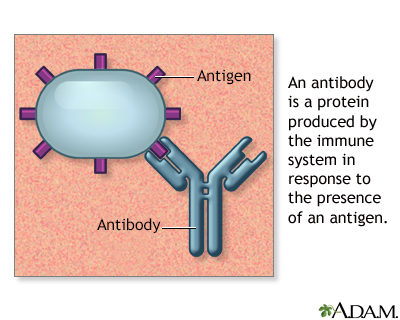
A drug allergy involves an immune response in the body that produces an allergic reaction to a medicine.
The first time you take the medicine, you may have no problems. But, your body's immune system may produce a substance (antibody) against that drug. The next time you take the drug, the antibody may tell your white blood cells to make a chemical called histamine. Histamines and other chemicals cause your allergy symptoms. The reaction of the body when a drug allergy is present generally involves special cells called B and T cell lymphocytes.
Common allergy-causing drugs include:
- Drugs used to treat seizures
- Insulin (especially animal sources of insulin)
- Substances containing iodine, such as x-ray contrast dyes (these can cause allergy-like reactions)
- Penicillin and related antibiotics
- Sulfa drugs
Most side effects of drugs are not due to an allergic reaction caused by the formation of IgE antibodies. For example, aspirin can cause hives or trigger asthma without involving the immune system. Many people confuse an unpleasant, but not serious, side effect of a medicine (such as nausea) with a drug allergy.
Symptoms
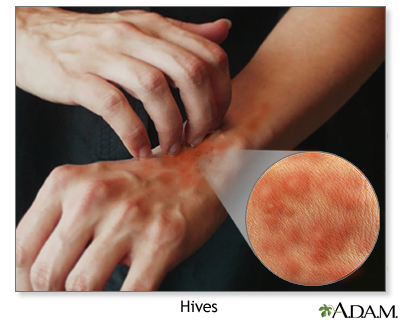
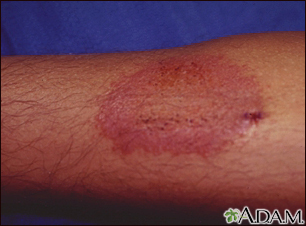
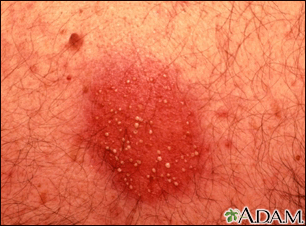
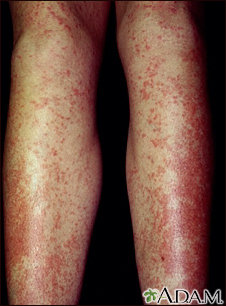
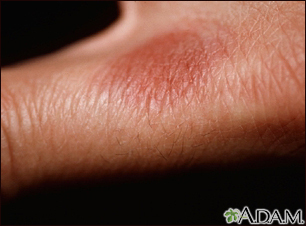
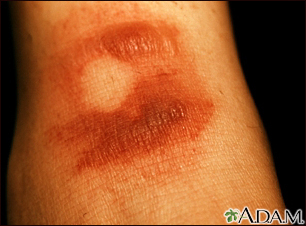
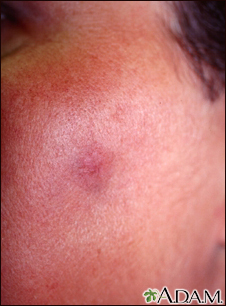
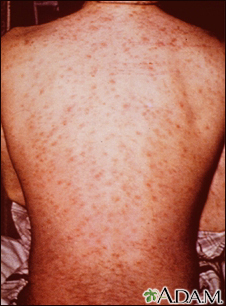
Most drug allergies cause minor skin rashes and hives. These symptoms may occur right away or hours after receiving the drug. Serum sickness is a delayed type of reaction that occurs a week or more after you are exposed to a medicine or vaccine. Drug allergies can also be associated with low blood counts.
Common symptoms of a drug allergy include:
- Hives
- Itching of the skin or eyes (common)
- Skin rash (common)
- Swelling of the lips, tongue, or face
- Wheezing
- Bleeding
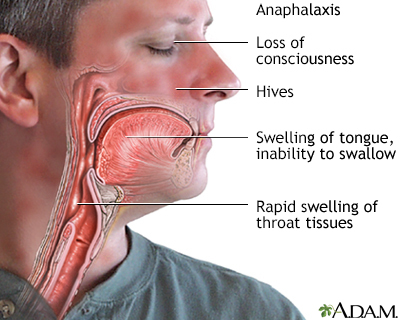
Symptoms of anaphylaxis include:
- Abdominal pain or cramping
- Confusion
- Diarrhea
- Difficulty breathing with wheezing or hoarse voice
- Dizziness
- Fainting, lightheadedness
- Hives over different parts of the body
- Nausea, vomiting
- Rapid pulse
- Sensation of feeling the heart beat (palpitations)
Exams and Tests
An examination may show:
- Decreased blood pressure
- Hives
- Rash
- Swelling of the lips, face, or tongue (angioedema)
- Wheezing
Skin testing may help diagnose an allergy to penicillin-type medicines. There are no good skin or blood tests to help diagnose other drug allergies.
If you have had allergy-like symptoms after taking a medicine or receiving contrast (dye) before getting an x-ray, your health care provider will often tell you that this is proof of a drug allergy. You do not need more testing.
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to relieve symptoms and prevent a severe reaction.
Treatment may include:
- Antihistamines to relieve mild symptoms such as rash, hives, and itching
- Bronchodilators such as albuterol to reduce asthma-like symptoms (moderate wheezing or cough)
- Corticosteroids applied to the skin, given by mouth, or given through a vein (intravenously)
- Epinephrine by injection to treat anaphylaxis
The offending medicine and similar drugs should be avoided. Make sure all your providers -- including dentists and hospital staff -- know about any drug allergies that you or your children have.
In some cases, a penicillin (or other drug) allergy responds to desensitization. This treatment involves being given very small doses at first, followed by larger and larger doses of a medicine to improve your tolerance of the drug. This process should be done only by an allergist, when there is no alternative drug for you to take.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most drug allergies respond to treatment. But sometimes, they can lead to severe asthma, anaphylaxis, or death.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you are taking a medicine and seem to be having a reaction to it.
Go to the emergency room or call the local emergency number (such as 911) if you have difficulty breathing or develop other symptoms of severe asthma or anaphylaxis. These are emergency conditions.
Prevention
There is generally no way to prevent a drug allergy.
If you have a known drug allergy, avoiding the drug is the best way to prevent an allergic reaction. You may also be told to avoid similar medicines.
In some cases, a provider may approve the use of a drug that causes an allergy if you are first treated with medicines that slow or block the immune response. These include corticosteroids (such as prednisone) and antihistamines. Do not try this without a provider's supervision. Pretreatment with corticosteroids and antihistamines has been shown to prevent allergic reactions in people who need to get x-ray contrast dye.
Your provider may also recommend desensitization.
Gallery
References
Barksdale AN, Muelleman RL. Allergy, hypersensitivity, and anaphylaxis. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 109.
Grammer LC. Drug allergy. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 239.
Solensky R, Phillips EJ. Drug allergy. In: Burks AW, Holgate ST, O'Hehir RE, et al, eds. Middleton's Allergy: Principles and Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 77.
