Living With Gastroparesis
When Melanie Dickens was 10 years old, she fell off a pair of stilts and injured her left leg. The injury triggered complex regional pain syndrome and led to…

Update your location to show providers, locations, and services closest to you.
Gastroparesis is a condition that reduces the ability of the stomach to empty its contents. It does not involve a blockage (obstruction).
Gastroparesis diabeticorum; Delayed gastric emptying; Diabetes - gastroparesis; Diabetic neuropathy - gastroparesis
The exact cause of gastroparesis is unknown. It may be caused by a disruption of nerve signals to the stomach. The condition is a common complication of diabetes. It can also follow some surgeries.
Risk factors for gastroparesis include:
Symptoms may include:
Tests you may need include:
People with diabetes should always control their blood sugar level. Better control of blood sugar level may improve symptoms of gastroparesis. Eating small and more frequent meals and soft foods may also help relieve some symptoms.
Medicines that may help include:
Other treatments may include:
Many treatments seem to provide only temporary benefit.
Ongoing nausea and vomiting may cause:
People with diabetes may have serious complications from poor blood sugar control.
Changes in your diet may help control symptoms. Contact your health care provider if symptoms continue or if you have new symptoms.
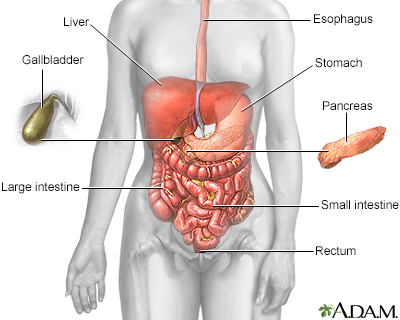
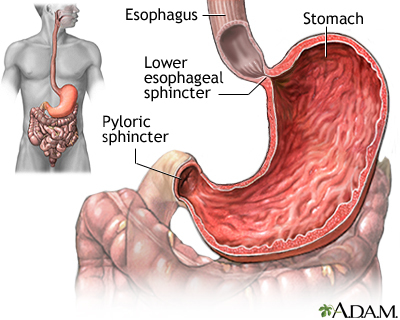
Bircher G, Woodrow G. Gastroenterology and nutrition in chronic kidney disease. In: Feehally J, Floege J, Tonelli M, Johnson RJ, eds. Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 86.
Koch KL. Gastric neuromuscular function and neuromuscular disorders. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 50.


When Melanie Dickens was 10 years old, she fell off a pair of stilts and injured her left leg. The injury triggered complex regional pain syndrome and led to…
