Definition
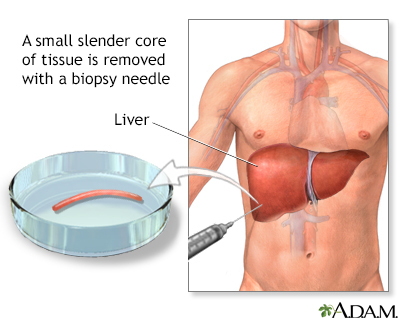
A liver biopsy is a test that takes a sample of tissue from the liver for examination.
Alternative Names
Biopsy - liver; Percutaneous liver biopsy; Needle biopsy of liver
How the Test is Performed
Most of the time, the test is done in the hospital. Before the test is done, you may be given a medicine to prevent pain or to calm you (sedative).
The biopsy may be done through the abdominal wall:
- You will lie on your back with your right hand under your head. You need to stay as still as you can.
- The health care provider will find the correct spot for the biopsy needle to be inserted into the liver. This is often done by using ultrasound.
- The skin is cleaned, and numbing medicine is injected into the area using a small needle.
- A small cut is made, and the biopsy needle is inserted.
- You will be told to hold your breath while the biopsy is taken. This is to reduce the chance of damage to the lung or liver.
- The needle is removed quickly.
- Pressure will be applied to stop the bleeding. A bandage is placed over the insertion site.
The procedure can also be done by inserting a needle into the jugular vein.
- If the procedure is performed this way, you will lie on your back.
- X-rays will be used to guide the provider to the vein.
- A special needle and catheter (thin tube) is used to take the biopsy sample.
If you receive sedation for this test, you will need someone to drive you home.
How to Prepare for the Test
Tell your provider about:
- Bleeding problems
- Drug allergies
- Medicines you are taking including herbs, supplements, or medicines you bought without a prescription
- Whether you are pregnant
You must sign a consent form. Blood tests are sometimes done to test your blood's ability to clot. You will be told not to eat or drink anything for the 8 hours before the test.
For infants and children:
The preparation needed for a child depends on the child's age and maturity. Your child's provider will tell you what you can do to prepare your child for this test.
How the Test will Feel
You will feel a stinging pain when the anesthetic is injected. The biopsy needle may feel like deep pressure and dull pain. Some people feel this pain in the shoulder.
Why the Test is Performed
The biopsy helps diagnose many liver diseases. The procedure also helps assess the stage (early, advanced) of liver disease. This is especially important in hepatitis B and C infection.
The biopsy also helps detect:
- Cancer
- Infections
- The cause of abnormal levels of liver enzymes that have been found in blood tests
- The cause of an unexplained liver enlargement
Normal Results
The liver tissue is normal.
What Abnormal Results Mean
The biopsy may reveal a number of liver diseases, including cirrhosis, hepatitis, or infections such as tuberculosis. It may also indicate cancer.
This test also may be performed for:
References
Bedossa P, Paradis V, Zucman-Rossi J. Cellular and molecular techniques. In: Burt AD, Ferrell LD, Hubscher SG, eds. MacSween's Pathology of the Liver. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 2.
Chernecky CC, Berger BJ. Liver biopsy (percutaneous liver biopsy) - diagnostic. In: Chernecky CC, Berger BJ, eds. Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures. 6th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders; 2013:727-729.
Holmes JA, Chung RT. Hepatitis C. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 80.
Martin P. Approach to the patient with liver disease. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 137.