Optic nerve atrophy
Definition
Optic nerve atrophy is damage to the optic nerve. The optic nerve carries images of what the eye sees to the brain.
Alternative Names
Optic atrophy; Optic neuropathy
Causes
There are many causes of optic atrophy. The most common is poor blood flow. This is called ischemic optic neuropathy. The problem most often affects older adults. The optic nerve can also be damaged by shock, toxins, radiation, and trauma.
Eye diseases, such as glaucoma, can also cause a form of optic nerve atrophy. The condition can also be caused by diseases of the brain and central nervous system. These may include:
- Brain tumor
- Cranial arteritis (sometimes called temporal arteritis or giant cell arteritis)
- Multiple sclerosis
- Stroke
There are also rare forms of hereditary optic nerve atrophy that affect children and young adults. Sometimes injuries to the face or head may result in optic nerve atrophy.
Symptoms
Optic nerve atrophy causes vision to dim and reduces the field of vision. The ability to see fine detail will also be lost. Colors will seem faded. Over time, the pupil will be less able to react to light, and eventually, its ability to react to light may be lost.
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will do a complete eye exam to look for the condition. The exam will include tests of:
- Color vision
- Pupil light reflex
- Tonometry
- Visual acuity
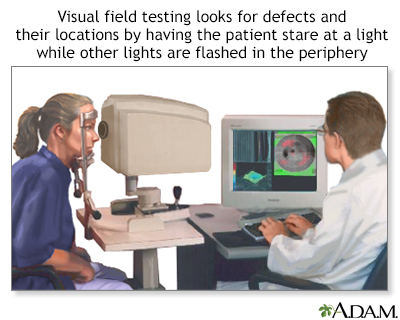
- Visual field (side vision) test
You may also need a complete physical exam and other tests.
Treatment
Damage from optic nerve atrophy cannot be reversed. The underlying disease must be found and treated. Otherwise, vision loss will continue.
Rarely, conditions that lead to optic atrophy may be treatable. Stem cells may prove helpful for people with optic atrophy.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Vision lost to optic nerve atrophy cannot be recovered. It is very important to protect the other eye.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
People with this condition need to be checked regularly by an eye doctor with experience in nerve-related conditions. Tell your doctor right away about any change in vision.
Prevention
Many causes of optic nerve atrophy cannot be prevented.
Prevention steps include:
- Older adults should have their provider carefully manage their blood pressure.
- Use standard safety precautions to prevent injuries to the face. Most facial injuries are the result of car accidents. Wearing seat belts may help prevent these injuries.
- Schedule a routine annual eye exam to check for glaucoma.
- Never drink home-brewed alcohol and forms of alcohol that are not intended for drinking. Methanol, which may be found in home-brewed alcohol, can cause optic nerve atrophy in both eyes.
Gallery
References
Cioffi GA, Liebmann JM. Diseases of the visual system. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 395.
Kahraman NS, Öner A. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell implantation in patients with optic atrophy. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2021;31(6):3463-3470. PMID: 33307808 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33307808/.
Karanjia R, Patel VR, Sadun AA. Hereditary, nutritional, and toxic optic atrophies. In: Yanoff M, Duker JS, eds. Ophthalmology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 9.9.
Thurtell MJ, Prasad S, Tomsak RL. Neuro-ophthalmology: afferent visual system. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 16.