Progeria
Definition
Progeria is a rare genetic condition that produces rapid aging in children.
Alternative Names
Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome; HGPS
Causes
Progeria is a rare condition. It is remarkable because its symptoms strongly resemble normal human aging, but it occurs in young children. In most cases, it is not passed down through families. It is rarely seen in more than one child in a family.
Symptoms
Symptoms include:
- Growth failure during the first year of life
- Narrow, shrunken or wrinkled face
- Baldness
- Loss of eyebrows and eyelashes
- Short stature
- Large head for size of face (macrocephaly)
- Open soft spot (fontanelle)
- Small jaw (micrognathia)
- Dry, scaly, thin skin
- Limited range of motion
- Teeth - delayed or absent formation
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam and order laboratory tests. This may show:
- Insulin resistance
- Skin changes similar to that seen in scleroderma (the connective tissue becomes tough and hardened)
- Generally normal cholesterol and triglyceride levels
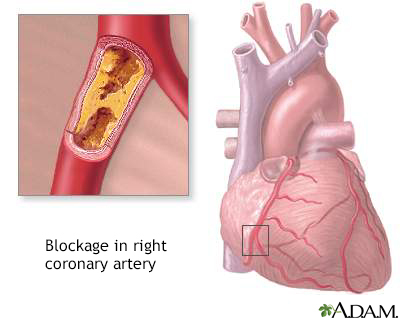
Cardiac stress testing may reveal signs of early atherosclerosis of blood vessels.
Genetic testing can detect changes in the gene (LMNA) that causes progeria.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for progeria. Aspirin and statin medicines may be used to protect against a heart attack or stroke.
Support Groups
Progeria Research Foundation, Inc. -- www.progeriaresearch.org
Outlook (Prognosis)
Progeria causes early death. People with the condition most often only live to their teenage years (average lifespan of 14 years). However, some can live into their early 20s. The cause of death is very often related to the heart or a stroke.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if your child does not appear to be growing or developing normally.
Gallery
References
Gordon LB. Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome (progeria). In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 109.
Gordon LB, Brown WT, Collins FS, et al. Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome. GeneReviews. 2015:1. PMID: 20301300 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20301300/. Updated January 17, 2019. November 1, 2021.