Definition
Shoulder pain is any pain in or around the shoulder joint.
Considerations
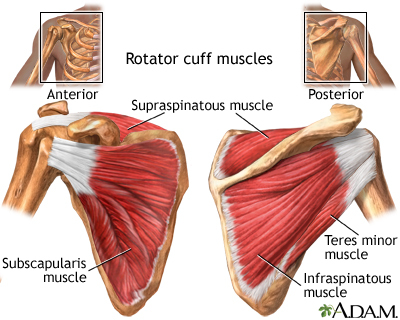
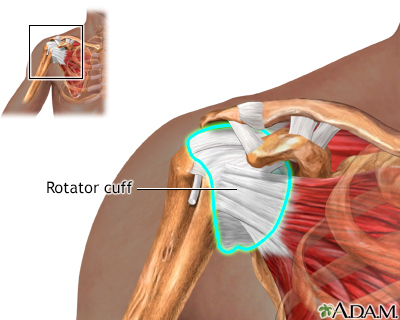
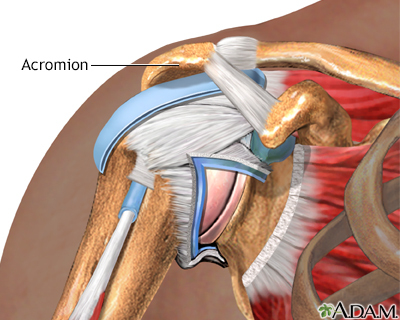
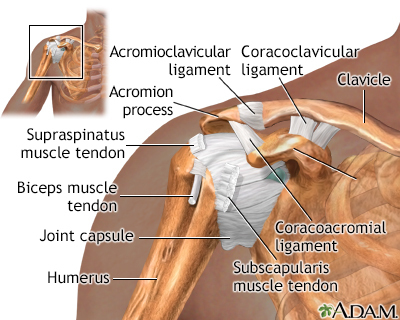
The shoulder is the most movable joint in the human body. A group of four muscles and their tendons, called the rotator cuff, give the shoulder its wide range of motion.
Swelling, damage, or bone changes around the rotator cuff can cause shoulder pain. You may have pain when lifting the arm above your head or moving it forward or behind your back.
Causes
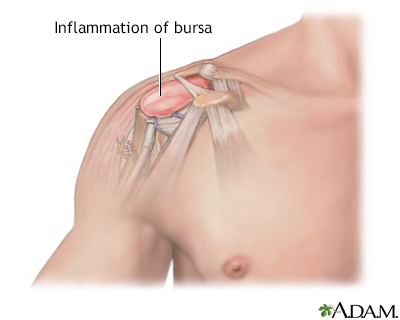
The most common cause of shoulder pain occurs when rotator cuff tendons become trapped under the bony area in the shoulder. The tendons become inflamed or damaged. This condition is called rotator cuff tendinitis or bursitis.
Shoulder pain may also be caused by:
- Arthritis in the shoulder joint
- Bone spurs in the shoulder area
- Bursitis, which is inflammation of a fluid-filled sac (bursa) that normally protects the joint and helps it move smoothly
- Broken shoulder bone
- Dislocation of the shoulder
- Shoulder separation
- Frozen shoulder, which occurs when the muscles, tendons, and ligaments inside the shoulder become stiff, making movement difficult and painful
- Overuse or injury of nearby tendons, such as the bicep muscles of the arms
- Nerve injury that leads to abnormal shoulder movement
- Tears of the rotator cuff tendons
- Poor shoulder posture and mechanics
Sometimes, shoulder pain may be due to a problem in another area of the body, such as the neck or lungs. This is called referred pain. There is usually pain at rest and no worsening of pain when moving the shoulder.
Home Care
Here are some tips for helping shoulder pain get better:
- Put ice on the shoulder area for 15 minutes, then leave it off for 15 minutes. Do this 3 to 4 times a day for 2 to 3 days. Wrap the ice in cloth. Do not put ice directly on the skin because this can result in frostbite.
- Rest your shoulder for the next few days.
- Slowly return to your regular activities. A physical therapist can help you do this safely.
- Taking ibuprofen or acetaminophen (such as Tylenol) may help reduce inflammation and pain.
Rotator cuff problems can be treated at home also.
- If you have had shoulder pain before, use ice and ibuprofen after exercising.
- Learn exercises to stretch and strengthen your rotator cuff tendons and shoulder muscles. A doctor or physical therapist can recommend such exercises.
- If you are recovering from tendinitis, continue to do range-of-motion exercises to avoid frozen shoulder.
- Practice good posture to keep your shoulder muscles and tendons in their right positions.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
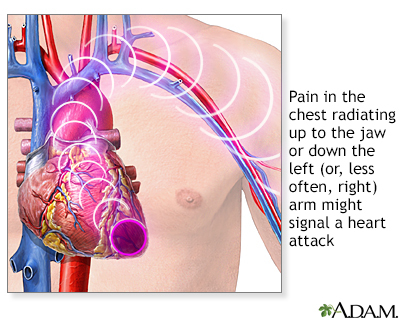
Sudden left shoulder pain can sometimes be a sign of a heart attack. Call 911 or your local emergency number if you have sudden pressure or crushing pain in your shoulder, especially if the pain runs from your chest to the left jaw, arm or neck, or occurs with shortness of breath, dizziness, or sweating.
Go to the hospital emergency room if you have just had a severe injury and your shoulder is very painful, swollen, bruised, or bleeding.
Call your health care provider if you have:
- Shoulder pain with a fever, swelling, or redness
- Problems moving the shoulder
- Pain for more than 2 to 4 weeks, even after home treatment
- Swelling of the shoulder
- Red or blue color of the skin of the shoulder area
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical exam and closely look at your shoulder. You will be asked questions to help the provider understand your shoulder problem.
Blood or imaging tests, such as x-rays or MRI, may be ordered to help diagnose the problem.
Your provider may recommend treatment for shoulder pain, including:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Injection of an anti-inflammatory medicine called corticosteroid
- Physical therapy
- Surgery if all other treatments do not work
If you have a rotator cuff problem, your provider will likely suggest self-care measures and exercises.
References
Gill TJ. Shoulder diagnosis and decision-making. In: Miller MD, Thompson SR, eds. DeLee, Drez, & Miller's Orthopaedic Sports Medicine: Principles and Practice. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 37.
Martin SD, Thornhill TS. Shoulder pain. In: Firestein GS, Budd RC, Gabriel SE, Koretzky GA, McInnes IB, O'Dell JR, eds. Firestein & Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 49.