Tarantula spider bite
Definition
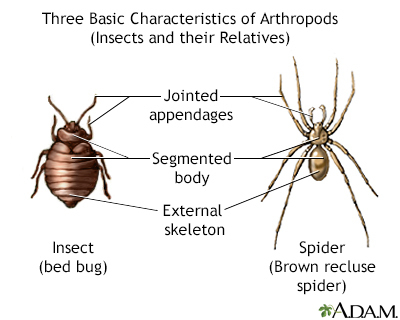
This article describes the effects of a tarantula spider bite or contact with tarantula hairs. The class of insects contains the largest number of venomous species known.
This article is for information only. DO NOT use it to treat or manage a tarantula spider bite. If you or someone you are with is bitten, call your local emergency number (such as 911), or your local poison center can be reached directly by calling the national toll-free Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) from anywhere in the United States.
Poisonous Ingredient
The venom of tarantulas found in the United States is not considered dangerous, but it may cause allergic reactions.
Where Found
Tarantulas are found across the southern and southwestern regions of the United States. Some people keep them as pets. As a group, they are found mainly in tropical and subtropical areas.
Symptoms
If a tarantula bites you, you may have pain at the site of the bite similar to a bee sting. The area of the bite may become warm and red. When one of these spiders is threatened, it rubs its hind legs across its own body surface and flicks thousands of tiny hairs toward the threat. These hairs have barbs that can pierce human skin. This causes causing swollen, itchy bumps to form. Itching may last for weeks.
If you are allergic to tarantula venom, these symptoms may occur:
- Breathing difficulty
- Loss of blood flow to major organs (an extreme reaction)
- Eyelid puffiness
- Itchiness
- Low blood pressure and collapse (shock)
- Rapid heart rate
- Skin rash
- Swelling at the site of the bite
- Swelling of the lips and throat
Home Care
Seek medical help right away.
Wash the area with soap and water. Place ice (wrapped in a clean cloth or other covering) on the site of the sting for 10 minutes and then off for 10 minutes. Repeat this process. If the person has blood flow problems, reduce the time the ice is used to prevent possible skin damage.
Before Calling Emergency
Have this information ready:
- Person's age, weight, and condition
- Type of spider, if possible
- Time of the bite
- Area of the body that was bitten
Poison Control
Your local poison center can be reached directly by calling the national toll-free Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) from anywhere in the United States. They will give you further instructions.
This is a free and confidential service. All local poison control centers in the United States use this national number. You should call if you have any questions about poisoning or poison prevention. It does NOT need to be an emergency. You can call for any reason, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
They will tell you if you should take the person to the hospital.
If possible, bring the spider to the emergency room for identification.
What to Expect at the Emergency Room
The health care provider will measure and monitor the person's vital signs, including temperature, pulse, breathing rate, and blood pressure. The wound and symptoms will be treated.
The person may receive:
- Blood and urine tests
- Breathing support, including oxygen, a tube through the mouth into the throat, and a breathing machine in serious cases.
- Chest x-ray
- ECG (electrocardiogram, or heart tracing)
- Intravenous fluids (IV, or through a vein)
- Medicines to treat symptoms
Any of the tiny hairs that remain on the skin can be removed with sticky tape.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Recovery most often takes about a week. Death from a tarantula spider bite in a healthy person is rare.
Gallery
References
Boyer LV, Binford GJ, Degan JA. Spider bites. In: Auerbach PS, Cushing TA, Harris NS, eds. Auerbach's Wilderness Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 43.
Otten EJ. Venomous animal injuries. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 55.