Definition
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin. Your body stores vitamin E in fatty tissue and the liver.
Alternative Names
Alpha-tocopherol; Gamma-tocopherol
Function
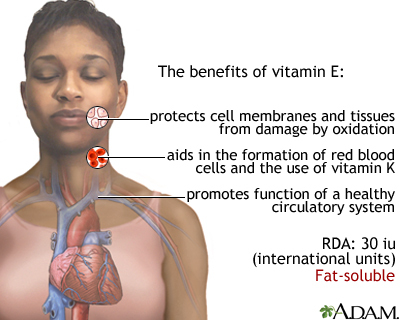
Vitamin E has the following functions:
- It is an antioxidant. This means it protects body tissue from damage caused by substances called free radicals. Free radicals can harm cells, tissues, and organs. They are believed to play a role in certain conditions related to aging.
- It helps keep the immune system strong against viruses and bacteria.
- It helps form red blood cells and widen blood vessels to keep blood from clotting inside them.
- It helps the body use vitamin K.
- Cells also use vitamin E to interact with each other. It helps them carry out many important functions.
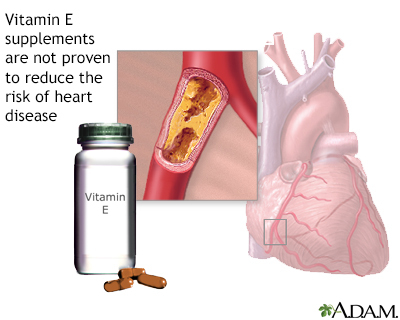
Whether vitamin E can prevent cancer, heart disease, dementia, liver disease, and stroke still requires further research.
Food Sources
The best way to get the daily requirement of vitamin E is by eating food sources. Vitamin E is found in the following foods:
- Vegetable oils (such as wheat germ, sunflower, safflower, corn, and soybean oils)
- Nuts (such as almonds, peanuts, and hazelnuts/filberts)
- Seeds (such as sunflower seeds)
- Green leafy vegetables (such as spinach and broccoli)
- Fortified breakfast cereals, fruit juices, margarine, and spreads.
Fortified means that vitamins have been added to the food. Check the Nutrition Fact Panel on the food label.
Products made from these foods, such as margarine, also contain vitamin E.
Side Effects
Eating vitamin E in foods is not risky or harmful. However, high doses of vitamin E supplements (alpha-tocopherol supplements) might increase the risk of bleeding in the brain (hemorrhagic stroke).
High levels of vitamin E may also increase the risk for birth defects. However, it needs more research.
Low intake may lead to hemolytic anemia in premature babies.
Recommendations
Recommendations for vitamin E, as well as other nutrients, are provided in the Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs) developed by the Food and Nutrition Board at the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. DRI is a term for a set of reference intakes that are used to plan and assess the nutrient intakes of healthy people. These values, which vary by age and sex, include:
Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA): The average daily level of intake that is enough to meet the nutrient needs of nearly all (97% to 98%) healthy people. An RDA is an intake level based on scientific research evidence.
Adequate Intake (AI): This level is established when there is not enough scientific research evidence to develop an RDA. It is set at a level that is thought to ensure enough nutrition.
Dietary reference intakes for vitamin E:
Infants (AI)
- 0 to 6 months: 4 mg/day
- 7 to 12 months: 5 mg/day
Children (RDA)
- 1 to 3 years: 6 mg/day
- 4 to 8 years: 7 mg/day
- 9 to 13 years: 11 mg/day
Adolescents and adults (RDA)
- 14 and older: 15 mg/day
- Pregnant teens and women: 15 mg/day
- Breastfeeding teens and women: 19 mg/day
Ask your health care provider which amount is best for you.
The highest safe level of vitamin E supplements for adults is 1,500 IU/day for natural forms of vitamin E, and 1,100 IU/day for the man-made (synthetic) form.
References
Markell M, Siddiqi HA. Vitamins and trace elements. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 27.
Mason JB, Booth SL. Vitamins, trace minerals, and other micronutrients. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 205.