Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome
Definition
Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome (WFS) is a group of symptoms caused when the adrenal glands fail to function normally. This occurs as a result of bleeding into the glands.
Alternative Names
Fulminant meningococcemia - Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome; Fulminant meningococcal sepsis - Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome; Hemorrhagic adrenalitis
Causes
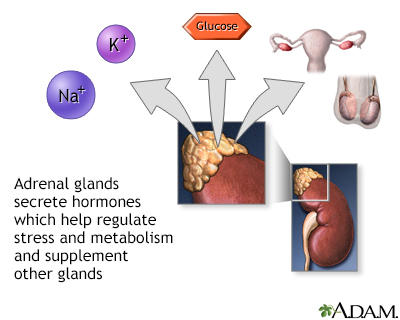
The adrenal glands are two triangle-shaped glands. One gland is located on top of each kidney. The adrenal glands produce and release different hormones that the body needs to function normally. The adrenal glands can be affected by many diseases, such as infections like WFS.
WFS is caused by severe infection with meningococcus bacteria or other bacteria such as:
- Group B streptococcus
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Staphylococcus aureus
Symptoms
Symptoms occur suddenly. They are due to the bacteria growing in number inside the body. Symptoms include:
- Fever and chills
- Joint and muscle pain
- Headache
- Vomiting
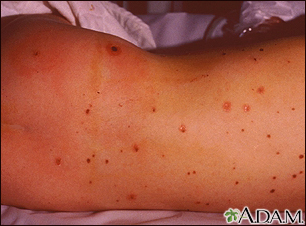
Infection with bacteria causes bleeding throughout the body, which causes:
- A rash throughout the body
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation in which small blood clots cut off blood supply to the organs
- Septic shock
Bleeding into the adrenal glands causes not enough adrenal hormones to be produced. This is called adrenal crisis, and it leads to symptoms such as:
- Dizziness, weakness
- Very low blood pressure
- Very fast heart rate
- Confusion or coma
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your symptoms.
Blood tests will be done to confirm a bacterial infection. Tests may include:
If the provider suspects the infection is caused by meningococcus bacteria, other tests that may be done include:
- Lumbar puncture to get a sample of spinal fluid for culture
- Skin biopsy and Gram stain
- Urine analysis
Tests that may be ordered to help diagnose acute adrenal crisis include:
Treatment
Antibiotics are started right away to treat the bacterial infection. Glucocorticoid medicines will also be given to treat adrenal gland insufficiency. Supportive treatments will be needed for other symptoms.
Outlook (Prognosis)
WFS is fatal unless treatment for the bacterial infection is started right away and glucocorticoid drugs are given.
Possible Complications
Prevention
To prevent WFS caused by meningococcal bacteria, a vaccine is available.
Gallery
References
Stephens DS. Neisseria meningitides. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 211.
Newell-Price JDC, Auchus RJ. The adrenal cortex. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 15.