Arterial insufficiency
Definition
Arterial insufficiency is any condition that slows or stops the flow of blood through your arteries. Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood from the heart to other places in your body.
Causes
One of the most common causes of arterial insufficiency is atherosclerosis or "hardening of the arteries." Fatty material (called plaque) builds up on the walls of your arteries. This causes them to become narrow and stiff. As a result, it is hard for blood to flow through your arteries.
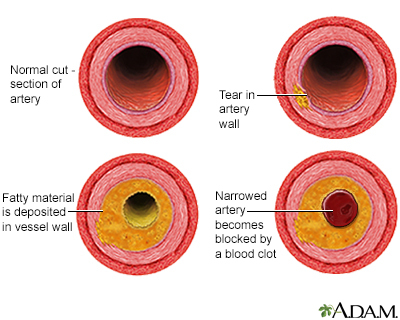
Blood flow may be suddenly stopped due to a blood clot. Clots can form on the plaque or, less often travel from another place such as the heart or other artery (also called embolus).
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on where your arteries become narrowed:
- If it affects your heart arteries, you may have chest pain (angina pectoris) or a heart attack.
- If it affects your brain arteries, you may have a transient ischemic attack (TIA) or stroke.
- If it affects the arteries that bring blood to your legs, you may have frequent leg cramping when you walk.
- If it affects the arteries in your belly area, you may have pain after you eat.
Gallery

References
Goodney PP. Clinical evaluation of the arterial system. In: Sidawy AN, Perler BA, eds. Rutherford's Vascular Surgery and Endovascular Therapy. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 18.
Libby P. The vascular biology of atherosclerosis. In: Zipes DP, Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann, DL, Tomaselli GF, Braunwald E, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 44.
