CMV retinitis
Definition
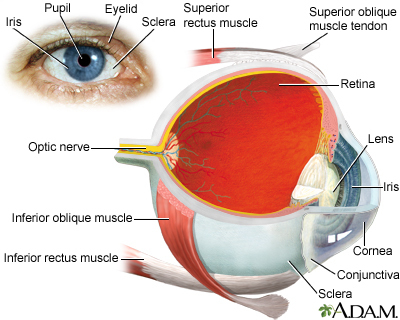
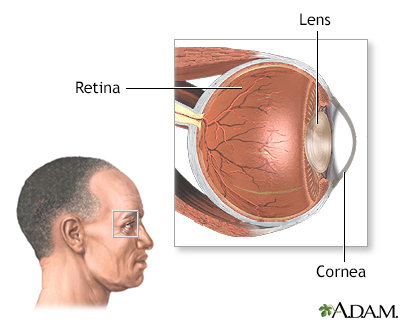
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis is a viral infection of the retina of the eye resulting in inflammation.
Alternative Names
Cytomegalovirus retinitis
Causes
CMV retinitis is caused by a member of a group of herpes-type viruses. Infection with CMV is very common. Most people are exposed to CMV in their lifetime, but typically only those with weakened immune systems become ill from CMV infection.
Serious CMV infections can occur in people who have weakened immune systems as a result of:
- HIV/AIDS
- Bone marrow transplant
- Chemotherapy
- Drugs that suppress the immune system
- Organ transplant
Symptoms
Some people with CMV retinitis have no symptoms.
If there are symptoms, they may include:
- Blind spots
- Blurred vision and other vision problems
- Floaters
Retinitis usually begins in one eye, but often progresses to the other eye. Without treatment, damage to the retina can lead to blindness in 4 to 6 months or less.
Exams and Tests
CMV retinitis is diagnosed through an ophthalmologic exam. Dilation of the pupils and ophthalmoscopy will show signs of CMV retinitis.
CMV infection may be diagnosed with blood or urine tests that look for substances specific to the infection. However, an infection may be present even with a negative blood or urine test. CMV can affect specific organs, such as the retina or gastrointestinal (GI) tract, and blood and urine tests can be negative. A tissue biopsy can detect the viral infection and presence of CMV virus particles, but this may be done only for some organs (GI Tract) and not others (eyes).
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to stop the virus from replicating and to stabilize or restore vision and prevent blindness. Long-term treatment is often needed. Medicines may be given by mouth (orally), through a vein (intravenously), or injected directly into the eye (intravitreously).
Outlook (Prognosis)
Even with treatment, the disease can worsen to blindness. This progression may happen because the virus becomes resistant to the antiviral drugs so the drugs are no longer effective, or because the person's immune system has deteriorated further.
CMV retinitis may also lead to retinal detachment, in which the retina detaches from the back of the eye, causing blindness.
Possible Complications
Complications that may result include:
- Kidney impairment (from medicines used to treat the condition)
- Low white blood cell count (from medicines used to treat the condition)
When to Contact a Medical Professional
If symptoms worsen or do not improve with treatment, or if new symptoms develop, contact your health care provider.
People with HIV/AIDS (especially those with a very low CD4 count) who have vision problems should make an appointment right away for an eye exam.
Prevention
A CMV infection usually only causes symptoms in people with a weakened immune system. Certain medicines (such as cancer therapy) and diseases (such as HIV/AIDS) can cause a weakened immune system.
People with AIDS who have a CD4 count of less than 250 cells/microliter or 250 cells/cubic millimeter should be examined regularly for this condition, even if they do not have symptoms. If you had CMV retinitis in the past, ask your provider if you need treatment to prevent its return.
Gallery

References
Britt WJ. Cytomegalovirus. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 137.
Freund KB, Sarraf D, Mieler WF, Yannuzzi LA. Infection. In: Freund KB, Sarraf D, Mieler WF, Yannuzzi LA, eds. The Retinal Atlas. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 5.