Flat bones
Definition
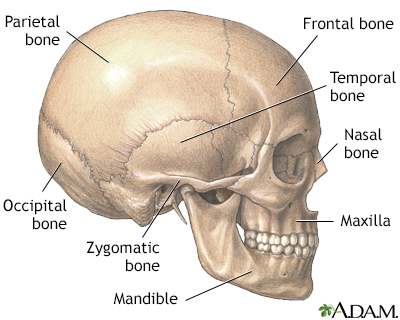
Flat bones are made up of a layer of spongy bone between two thin layers of compact bone. They have a flat shape, not rounded. Examples include the skull and rib bones. Flat bones have marrow, but they do not have a bone marrow cavity.
Gallery
References
Standring S. The skull. In: Standring S, ed. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 42nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 34.
Standring S. Chest wall and breast. In: Standring S, ed. Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 42nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 53.