Hemolytic disease of the newborn
Definition
Hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) is a blood disorder in a fetus or newborn infant. In some infants, it can be fatal.
Normally, red blood cells (RBCs) last for about 120 days in the body. In this disorder, RBCs in the blood are destroyed quickly and thus do not last as long.
Alternative Names
Hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN); Erythroblastosis fetalis; Anemia - HDN; Blood incompatibility - HDN; ABO incompatibility - HDN; Rh incompatibility - HDN
Causes
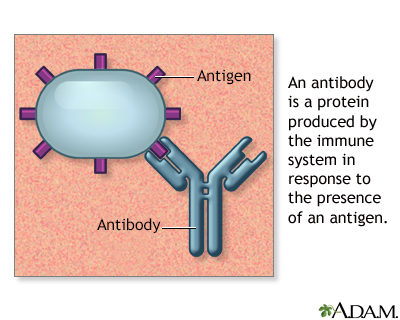
During pregnancy, RBCs from the unborn baby can cross into the mother's blood through the placenta. HDN occurs when the immune system of the mother sees a baby's RBCs as foreign. Antibodies then develop against the baby's RBCs. These antibodies attack the RBCs in the baby's blood and cause them to break down too early.
HDN may develop when a mother and her unborn baby have different blood types. The types are based on small substances (antigens) on the surface of the blood cells.
There is more than one way in which the unborn baby's blood type may not match the mother's.
- A, B, AB, and O are the 4 major blood group antigens or types. This is the most common form of a mismatch. In most cases, this is not very severe.
- Rh is short for the "rhesus" antigen or blood type. People are either positive or negative for this antigen. If the mother is Rh-negative and the baby in the womb has Rh-positive cells, her antibodies to the Rh antigen can cross the placenta and cause very severe anemia in the baby. It can be prevented in most cases.
- There are other, much less common, types of mismatch between minor blood group antigens. Some of these can also cause severe problems.
Symptoms
HDN can destroy the newborn baby's blood cells very quickly, which can cause symptoms such as:
- Edema (swelling under the surface of the skin)
- Newborn jaundice which occurs sooner and is more severe than normal
Exams and Tests
Signs of HDN include:
- Anemia or low blood count
- Enlarged liver or spleen
- Hydrops (fluid throughout the body's tissues, including in the spaces containing the lungs, heart, and abdominal organs), which can lead to heart failure or respiratory failure from too much fluid
Which tests are done depends on the type of blood group incompatibility and the severity of symptoms, but may include:
- Complete blood count and immature red blood cell (reticulocyte) count
- Bilirubin level
- Blood typing
Treatment
Infants with HDN may be treated with:
- Feeding often and receiving extra fluids.
- Light therapy (phototherapy) using special blue lights to convert bilirubin into a form which is easier for the baby's body to get rid of.
- Antibodies (intravenous immunoglobulin, or IVIG) to help protect the baby's red cells from being destroyed.
- Medicines to raise blood pressure if it drops too low.
- In severe cases, an exchange transfusion may need to be performed. This involves removing a large amount of the baby's blood, and thus the extra bilirubin and antibodies. Fresh donor blood is infused.
- Simple transfusion (without exchange). This may need to be repeated after the baby goes home from the hospital.
Outlook (Prognosis)
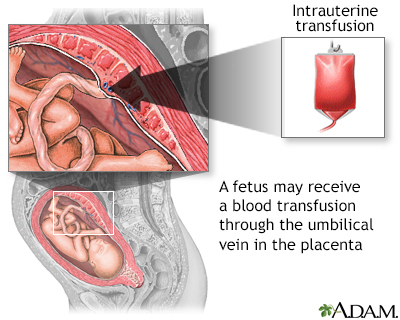
The severity of this condition can vary. Some babies have no symptoms. In other cases, problems such as hydrops can cause the baby to die before, or shortly after, birth. Severe HDN may be treated before birth by intrauterine blood transfusions.
Prevention
The most severe form of this disease, which is caused by Rh incompatibility, can be prevented if the mother is tested during pregnancy. If needed, she is given a shot of a medicine called RhoGAM at certain times during and after her pregnancy. If you have had a baby with this disease, talk with your health care provider if you plan to have another baby.
Gallery
References
Josephson CD, Sloan SR. Pediatric transfusion medicine. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 121.
Niss O, Ware RE. Blood disorders. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 124.
Simmons PM, Magann EF. Immune and non-immune hydrops fetalis. In: Martin RJ, Fanaroff AA, Walsh MC, eds. Fanaroff and Martin's Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine: Diseases of the Fetus and Infant. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 23.