Heterochromia
Definition
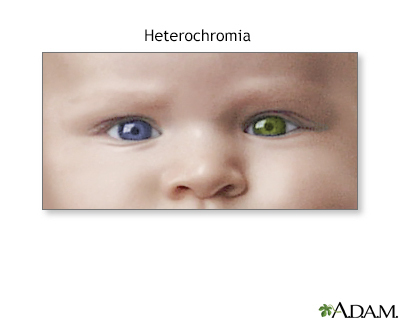
Heterochromia is different colored eyes in the same person.
Alternative Names
Differently colored eyes; Eyes - different colors
Considerations
Heterochromia is uncommon in humans. However, it is quite common in dogs (such as Dalmatians and Australian sheep dogs), cats, and horses.
Causes
Most cases of heterochromia are hereditary, caused by a disease or syndrome, or due to an injury. Sometimes, one eye may change color following certain diseases or injuries.
Specific causes of eye color changes include:
- Bleeding (hemorrhage)
- Familial heterochromia
- Foreign object in the eye
- Glaucoma, or some medicines used to treat it
- Injury
- Mild inflammation affecting only one eye
- Neurofibromatosis
- Waardenburg syndrome
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Talk to your health care provider if you notice new changes in the color of one eye, or two differently colored eyes in your infant. A thorough eye exam is needed to rule out a medical problem.
Some conditions and syndromes associated with heterochromia, such as pigmentary glaucoma, can only be detected by a thorough eye exam.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider may ask the following questions to help evaluate the cause:
- Did you notice the two different eye colors when the child was born, shortly after the birth, or recently?
- Are any other symptoms present?
An infant with heterochromia should be examined by both a pediatrician and an ophthalmologist for other possible problems.
A complete eye exam can rule out most causes of heterochromia. If there doesn't seem to be an underlying disorder, no further testing may be needed. If another disorder is suspected diagnostic tests, such as blood tests or chromosome studies, may be done to confirm the diagnosis.
Gallery
References
Nischal KK. Ophthalmology. In: Zitelli BJ, McIntire SC, Nowalk AJ, Garrison J, eds. Zitelli and Davis' Atlas of Pediatric Physical Diagnosis. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 20.
Olitsky SE, Marsh JD. Abnormalities of pupil and iris. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 640.
Örge FH. Examination and common problems of the neonatal eye. In: Martin RJ, Fanaroff AA, Walsh MC, eds. Fanaroff and Martin's Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 95.