Lordosis - lumbar
Definition
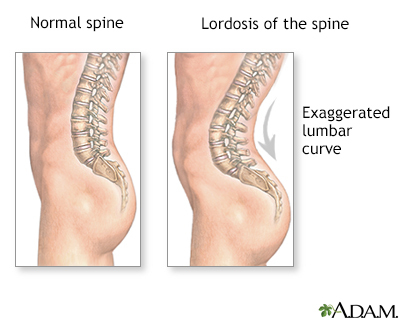
Lordosis is the inward curve of the lumbar spine (just above the buttocks). A small degree of lordosis is normal. Too much curving is called swayback.
Alternative Names
Swayback; Arched back; Lordosis - lumbar
Causes
Lordosis tends to make the buttocks appear more prominent. Children with hyperlordosis will have a large space underneath the lower back when lying face up on a hard surface.
Some children have marked lordosis, but, most often fixes itself as the child grows. This is called benign juvenile lordosis.
Spondylolisthesis may cause lordosis. In this condition, a bone (vertebra) in the spine slips out of the proper position onto the bone below it. You may be born with this. It can develop after certain sports activities, such as gymnastics. It may develop along with arthritis in the spine.
Much less common causes in children include:
- Achondroplasia, a disorder of bone growth that causes the most common type of dwarfism
- Muscular dystrophy
- Other genetic conditions
Home Care
Most of the time, lordosis is not treated if the back is flexible. It is not likely to progress or cause problems.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you notice that your child has an exaggerated posture or a curve in the back. Your provider must check to see if there is a medical problem.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
The provider will do a physical exam. To examine the spine, your child may have to bend forward, to the side, and to lie flat on a table. If the lordotic curve is flexible (when the child bends forward the curve reverses itself), it is generally not a concern. If the curve does not move, medical evaluation and treatment are needed.
Other tests may be needed, particularly if the curve seems "fixed" (not bendable). These may include:
- Lumbosacral spine x-ray
- Other tests to rule out disorders that could be causing the condition
- MRI of the spine
- Laboratory tests
Gallery
References
Mistovich RJ, Spiegel DA. The spine. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 699.
Warner WC, Sawyer JR. Scoliosis and kyphosis. In: Azar FM, Beaty JH, eds. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 44.