Pharyngitis - sore throat
Definition
Pharyngitis, or sore throat, is discomfort, pain, or scratchiness in the throat. It often makes it painful to swallow.
Patient Education Video: Pharyngitis
Alternative Names
Pharyngitis - bacterial; Sore throat
Causes
Pharyngitis is caused by swelling in the back of the throat (pharynx) between the tonsils and the voice box (larynx).
Most sore throats are caused by colds, the flu, coxsackie virus or mono (mononucleosis).
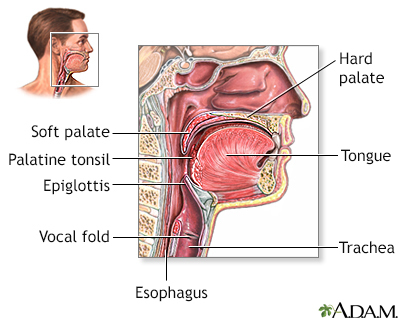
Bacteria that can cause pharyngitis in some cases:
- Strep throat is caused by group A streptococcus.
- Less commonly, bacterial diseases such as gonorrhea and chlamydia can cause sore throat.
Most cases of pharyngitis occur during the colder months. The illness often spreads among family members and close contacts.
Symptoms
The main symptom is a sore throat.
Other symptoms may include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Joint pain and muscle aches
- Skin rashes
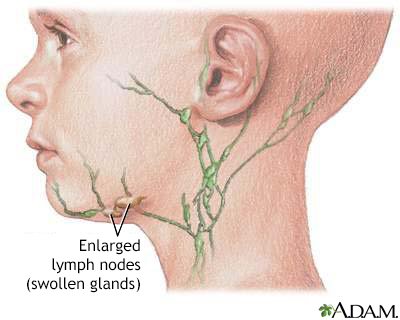
- Swollen lymph nodes (glands) in the neck
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam and look at your throat.
A rapid test or throat culture to test for strep throat may be done. Other laboratory tests may be done, depending on the suspected cause.
Treatment
Most sore throats are caused by viruses. Antibiotics do not help viral sore throats. Using these medicines when they are not needed leads to antibiotics not working as well when they are needed.
Sore throat is treated with antibiotics if:
- A strep test or culture is positive. Your provider cannot diagnose strep throat by symptoms or a physical exam alone.
- A culture for chlamydia or gonorrhea is positive.
Sore throat caused by the flu (influenza) may be helped by antiviral medicines.
The following tips may help your sore throat feel better:
- Drink soothing liquids. You can either drink warm liquids, such as lemon tea with honey, or cold liquids, such as ice water. You could also suck on a fruit-flavored ice pop.
- Gargle several times a day with warm salt water (1/2 tsp or 3 grams of salt in 1 cup or 240 milliliters of water).
- Suck on hard candies or throat lozenges. Young children should not be given these products because they can choke on them.
- Use of a cool-mist vaporizer or humidifier can moisten the air and soothe a dry and painful throat.
- Try over-the-counter pain medicines, such as acetaminophen.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You develop a sore throat that does not go away after several days
- You have a high fever, swollen lymph nodes in your neck, or a rash
Seek medical care right away if you have a sore throat and trouble breathing.
Gallery

References
Flores AR, Caserta MT. Pharyngitis. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 59.
Harris AM, Hicks LA, Qaseem A; High Value Care Task Force of the American College of Physicians and for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Appropriate antibiotic use for acute respiratory tract infection in adults: advice for high-value care from the American College of Physicians and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Ann Intern Med. 2016;164(6):425-434. PMID: 26785402 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26785402/.
Shulman ST, Bisno AL, Clegg HW, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and management of group A streptococcal pharyngitis: 2012 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;55(10):e86-e102. PMID: 22965026 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22965026/.
Tanz RR. Acute pharyngitis. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 409.
van Driel ML, De Sutter AI, Habraken H, Thorning S, Christiaens T. Different antibiotic treatments for group A streptococcal pharyngitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;9:CD004406. PMID: 27614728 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27614728/.