Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome
Definition
Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome is a group of defects passed down through families. The disorder involves the skin, nervous system, eyes, endocrine glands, urinary and reproductive systems, and bones.
It causes an unusual facial appearance and a higher risk for skin cancers and noncancerous tumors.
Alternative Names
NBCC syndrome; Gorlin syndrome; Gorlin-Goltz syndrome; Basal cell nevus syndrome (BCNS); Basal cell cancer - nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome
Causes
Nevoid basal cell carcinoma nevus syndrome is a rare genetic condition. The main gene linked to the syndrome is known as PTCH ("patched"). A second gene, called SUFU, has also been associated with this condition.
Abnormalities in these genes are most commonly passed down through families as an autosomal dominant trait. This means you develop the syndrome if either parent passes the gene to you. If either of your parents has this syndrome, you have a 50 percent chance of having it. It is also possible to develop this gene defect with no family history.
Symptoms
Main symptoms of this disorder are:
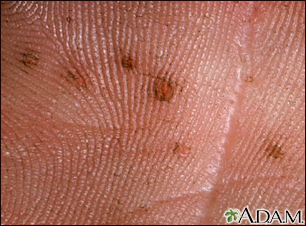
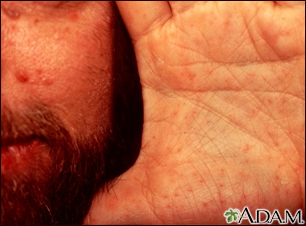
- A type of skin cancer called basal cell carcinoma that develops around the time of puberty
- A noncancerous tumor of the jaw, called kerotocystic odontogenic tumor that also develops during puberty
Other symptoms include:
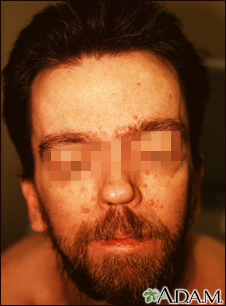
- Broad nose
- Cleft palate
- Heavy, protruding brow
- Jaw that sticks out (in some cases)
- Wide-set eyes
- Pitting on palms and soles
The condition may affect the nervous system and lead to:
- Eye problems
- Deafness
- Intellectual disability
- Seizures
- Tumors of the brain
The condition also leads to bone defects, including:
- Curvature of the back (scoliosis)
- Severe curvature of the back (kyphosis)
- Abnormal ribs
Exams and Tests
There may be a family history of this disorder and a past history of basal cell skin cancers.
Tests may reveal:
- Brain tumors
- Cysts in the jaw, which can lead to abnormal tooth development or jaw fractures
- Defects in the colored part (iris) or lens of the eye
- Head swelling due to fluid on the brain (hydrocephalus)
- Rib abnormalities
Tests that may be done include:
- Echocardiogram of the heart
- Genetic testing (in some patients)
- MRI of the brain
- Skin biopsy of tumors
- X-rays of the bones, teeth, and skull
- Ultrasound to check for ovarian tumors
Treatment
It is important to get examined by a skin doctor (dermatologist) often, so that skin cancers may be treated while they are still small.
People with this disorder may also be seen and treated by other specialists, depending on which part of the body is affected. For example, a cancer specialist (oncologist) may treat tumors in the body, and an orthopedic surgeon may help treat bone problems.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Frequent follow-up with a variety of specialist doctors is important for having a good outcome.
Possible Complications
People with this condition may develop:
- Blindness
- Brain tumor
- Deafness
- Fractures
- Ovarian tumors
- Cardiac fibromas
- Skin damage and severe scarring due to skin cancers
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider for an appointment if:
- You or any family members have nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome, especially if you are planning to have a child.
- You have a child who has symptoms of this disorder.
Prevention
Couples with a family history of this syndrome might consider genetic counseling before becoming pregnant.
Staying out of the sun and using sunscreen can help prevent new basal cell skin cancers.
Avoid radiation such as x-rays. People with this condition are very sensitive to radiation. Exposure to radiation can lead to skin cancers.
Gallery

References
Epstein EH. Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (Gorlin syndrome). In: Lebwohl MG, Heymann WR, Coulson IH, Murrell DF, eds. Treatment of Skin Disease: Comprehensive Therapeutic Strategies. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 170.
Hirner JP, Martin KL. Tumors of the skin. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 690.
Walsh MF, Cadoo K, Salo-Mullen EE, Dubard-Gault M, Stadler ZK, Offit K. Genetic factors: hereditary cancer predisposition syndromes. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Kastan MB, Doroshow JH, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloff's Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 13.