Vehicle Heat Safety for Children
Unfortunately, child deaths and heat-related illness, like dying from heatstroke in a hot car, increase during summer. Since 1998, more than 950 children have…

Update your location to show providers, locations, and services closest to you.
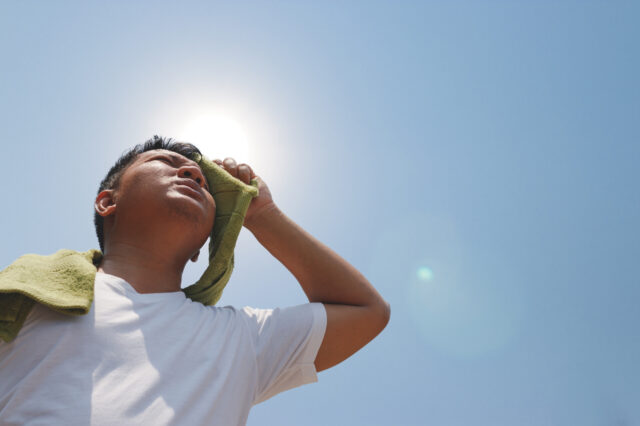
Heat emergencies or illnesses are caused by exposure to extreme heat and sun. Heat illnesses can be prevented by being careful in hot, humid weather.
Heatstroke; Heat illness; Dehydration - heat emergency
Heat injuries can occur due to high temperatures and humidity. You are more likely to feel the effects of heat sooner if:
The following make it harder for the body to regulate its temperature, and make a heat emergency more likely:
Muscle cramps are the first stage of heat illness. If heat exposure continues and these symptoms are not treated, they can lead to heat exhaustion and then heat stroke.
Heat stroke occurs when the body is no longer able to regulate its temperature, and it keeps rising. Heat stroke can cause shock, brain damage, organ failure, and even death.
The early symptoms of heat illness include:
Later symptoms of heat exhaustion include:
The symptoms of heatstroke include those of heat exhaustion in combination with very high body temperature and significant neurologic symptoms (call 911 or the local emergency number right away):
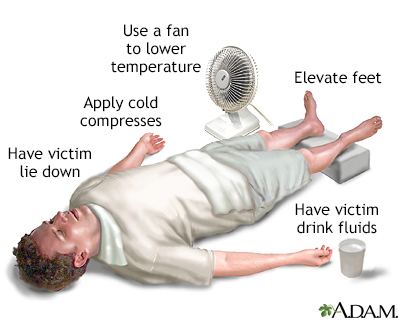
If you think a person may have heat illness or emergency:
Follow these precautions:
Call 911 or the local emergency number if:
The first step in preventing heat illnesses is thinking ahead.
To help prevent heat illnesses:
After recovering from exertional heat illness, check with your health care provider for advice before returning to heavy exertion. Begin exercise in a cool environment and slowly increase the degree of heat. Over several weeks, increase how long and how hard you exercise, as well as the amount of heat.
Landry GL. Heat Injuries. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 710.
O'Brien KK, Leon LR, Kenefick RW, O'Connor FG. Clinical management of heat-related illnesses. In: Auerbach PS, Cushing TA, Harris NS, eds. Auerbach's Wilderness Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 13.
Platt M, Price MG. Heat illness. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 133.
Prendergast HM, Erickson TB. Procedures pertaining to hypothermia and hyperthermia. In: Roberts JR, Custalow CB, Thomsen TW, eds. Roberts and Hedges' Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 65.
Sawka MN, O'Connor FG. Disorders due to heat and cold. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 101.

Unfortunately, child deaths and heat-related illness, like dying from heatstroke in a hot car, increase during summer. Since 1998, more than 950 children have…

This Fourth of July holiday weekend, we saw not only record travel but record-breaking heat across the South, with heat indexes reaching 115-plus degrees and…
