Hydrocele repair
Definition
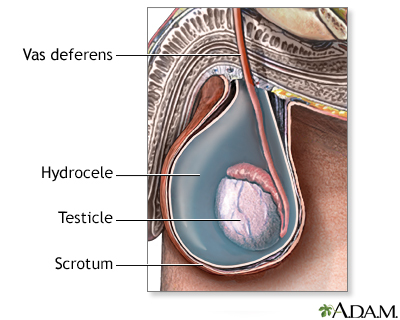
Hydrocele repair is surgery to correct the swelling of the scrotum that occurs when you have a hydrocele. A hydrocele is a collection of fluid around a testicle.
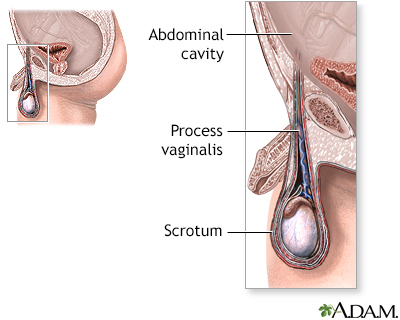
Baby boys sometimes have a hydrocele at birth. Hydroceles also occur in older boys and men. Sometimes they form when there is also a hernia (an abnormal bulging of tissue) present. Hydroceles are fairly common.
Alternative Names
Hydrocelectomy
Description
Surgery to repair a hydrocele is often done at an outpatient clinic. General anesthesia is used so you will be asleep and pain-free during the procedure.
In a baby or child:
- The surgeon makes a small surgical cut in the fold of the groin, and then drains the fluid. The sac (hydrocele) holding the fluid may be removed. The surgeon strengthens the muscle wall with stitches. This is called a hernia repair.
- Sometimes the surgeon uses a laparoscope to do this procedure. A laparoscope is a tiny camera that the surgeon inserts into the area through a small surgical cut. The camera is attached to a video monitor. The surgeon makes the repair with small instruments that are inserted through other small surgical cuts.
In adults:
- The cut is most often made on the scrotum. The surgeon then drains the fluid after removing part of the hydrocele sac.
Needle drainage of the fluid is not done very often because the problem will always come back.
Why the Procedure Is Performed
Hydroceles often go away on their own in children, but not in adults. Most hydroceles in infants will go away by the time they are 2 years old.
Your surgeon may recommend hydrocele repair if the hydrocele:
- Becomes too large
- Causes problems with blood flow
- Is infected
- Is painful or uncomfortable
The repair may also be done if there is a hernia associated with the problem.
Risks
Risks for any anesthesia are:
- Allergic reactions to medicines
- Breathing problems
Risks for any surgery are:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Recurrence of the hydrocele
Before the Procedure
Always tell your health care provider what drugs you are taking, even drugs, supplements, or herbs you bought without a prescription. Also tell your provider if you have any drug allergies or if you have had bleeding problems in the past.
Several days before surgery, adults may be asked to stop taking aspirin or other drugs that affect blood clotting. These include ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil), naproxen (Naprosyn, Aleve), some herbal supplements, and others.
You or your child may be asked to stop eating and drinking at least 6 hours before the procedure.
Take the medicines you have been told to take with a small sip of water.
After the Procedure
Recovery is quick in most cases. Most people can go home a few hours after surgery. Children should limit activity and get extra rest in the first few days after surgery. In most cases, normal activity can start again in about 4 to 7 days.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The success rate for hydrocele repair is very high. The long-term outlook is excellent. However, another hydrocele may form over time, especially if a hernia was present.
Gallery
References
Aiken JJ. Inguinal hernias. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 373.
Cancian MJ, Caldamone AA. Special considerations in the pediatric patient. In: Taneja SS, Shah O, eds. Taneja's Complications of Urologic Surgery. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 54.
Hawksworth DJ, Khera M, Herati AD. Surgery of the scrotum and seminal vesicles. In: Partin AW, Domochowski RR, Kavoussi LR, Peters CA, eds. Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 83.
Palmer LS, Palmer JS. Management of abnormalities of the external genitalia in boys. In: Partin AW, Domochowski RR, Kavoussi LR, Peters CA, eds. Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 44.