Finding Answers: Robyn’s Journey to Overcoming Infertility
As a newlywed, Robyn Broxton enjoyed crossing off bucket list items with her husband. Now, as a mother to two daughters, she enjoys finding fun, memorable…

Update your location to show providers, locations, and services closest to you.
A pregnancy test measures a hormone in the body called human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG or hCG). HCG is a hormone produced during pregnancy. It appears in the blood and urine of pregnant women as early as 10 days after conception.
A pregnancy test is done using blood or urine. There are 2 types of blood tests:
The blood test is done by drawing a single tube of blood and sending it to a laboratory. You may wait anywhere from a few hours to more than a day to get the results.
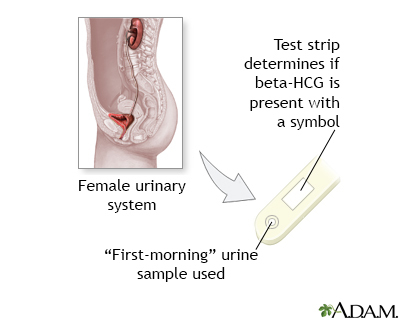
The urine HCG test is most often performed by placing a drop of urine on a prepared chemical strip. It takes 1 to 2 minutes for a result.
For the urine test, you urinate into a cup.
For the blood test, the health care provider uses a needle and syringe to draw blood from your vein into a tube. Any discomfort you might feel from the blood draw will only last a few seconds.
For the urine test, you urinate into a cup.
For the blood test, the provider uses a needle and syringe to draw blood from your vein into a tube. Any discomfort you might feel from the blood draw will only last a few seconds.
This test is done to:
HCG level rises rapidly during the first trimester of pregnancy and then slightly declines.
HCG level should almost double every 48 hours in the beginning of a pregnancy. An HCG level that does not rise appropriately may indicate a problem with your pregnancy. Problems related to an abnormal rising HCG level include miscarriage and ectopic (tubal) pregnancy.
An extremely high level of HCG may suggest a molar pregnancy or more than one fetus, for example, twins.
Your provider will discuss the meaning of your HCG level with you.
Urine pregnancy tests will only be positive when you have enough HCG in your blood. Most over-the-counter home pregnancy tests will not show that you are pregnant until your expected menstrual cycle is late. Testing before this will often give an inaccurate result. The HCG level is higher if your urine is more concentrated. A good time to test is when you first get up in the morning.
If you think you are pregnant, repeat the pregnancy test at home or at your provider's office.
Jeelani R, Bluth MH. Reproductive function and pregnancy. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 26.
Warner EA, Herold AH. Interpreting laboratory tests. In: Rakel RE, Rakel DP, eds. Textbook of Family Medicine. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 14.
As a newlywed, Robyn Broxton enjoyed crossing off bucket list items with her husband. Now, as a mother to two daughters, she enjoys finding fun, memorable…

“Everything grows rounder and wider and weirder, and I sit here in the middle of it all and wonder who in the world you will turn out to be.” — Carrie Fisher…

We’ve come a long way from the one-line-two-line pregnancy tests of the past. Today, many tests even manage to come up with the words “pregnant” or “not pregnant.” But now, in one of the biggest...