Undescended testicle
Definition
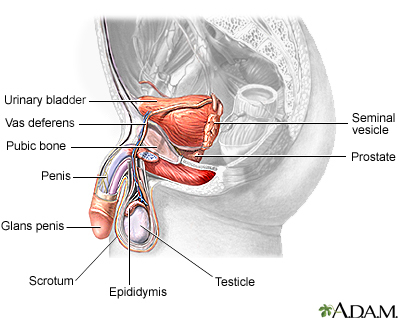
Undescended testicle occurs when one or both testicles fail to move into the scrotum before birth.
Alternative Names
Cryptorchidism; Empty scrotum - undescended testes; Scrotum - empty (undescended testes); Monorchism; Vanished testes - undescended; Retractile testes
Causes
Most of the time, a boy's testicles descend by the time he is 9 months old. Undescended testicles are common in infants who are born early. The problem occurs less in full-term infants.
Some babies have a condition called retractile testes and the health care provider may not be able to find the testicles. In this case, the testicle is normal, but is pulled back out of the scrotum by a muscle reflex. This occurs because the testicles are still small before puberty. The testicles will descend normally at puberty and surgery is not needed.
Testicles that do not naturally descend into the scrotum are considered abnormal. An undescended testicle is more likely to develop cancer, even if it is brought into the scrotum with surgery. Cancer is also more likely in the other testicle.
Bringing the testicle into the scrotum can improve sperm production and increase the chances of good fertility. It also allows the provider to do an exam for the early detection of cancer.
In other cases, no testicle may be found, even during surgery. This may be due to a problem that occurred while the baby was still developing before birth.
Symptoms
Most of the time there are no symptoms other than the absence of the testicle in the scrotum. (This is called an empty scrotum.)
Exams and Tests
An exam by the provider confirms that one or both of the testicles are not in the scrotum.
The provider may or may not be able to feel the undescended testicle in the abdominal wall above the scrotum.
Imaging tests, such as an ultrasound or CT scan, may be done.
Treatment
In most cases, the testicle will descend without treatment during the child's first year. If this does not occur, treatment may include:
- Hormone injections (B-HCG or testosterone) to try to bring the testicle into the scrotum.
- Surgery (orchiopexy) to bring the testicle into the scrotum. This is the main treatment.
Having surgery early may prevent damage to the testicles and avoid infertility. An undescended testicle that is found later in life may need to be removed. This is because the testicle is not likely to function well and could pose a risk for cancer.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most of the time, the problem goes away without treatment. Medicine or surgery to correct the condition is successful in most cases. Once the condition is corrected, you should have routine testicle exams by your doctor.
In about 50% of males with undescended testicles, the testicles cannot be found at the time of surgery. This is called a vanished or absent testis. As stated earlier, it may be due to something while the baby was still developing during pregnancy.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Damage to the testicle from surgery
- Infertility later in life
- Testicular cancer in one or both testes
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your child's provider if he appears to have an undescended testicle.
Gallery
References
Barthold JS, Hagerty JA. Etiology, diagnosis, and management of the undescended testis. In: Partin AW, Domochowski RR, Kavoussi LR, Peters CA, eds. Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 46.
Chung DH. Pediatric surgery. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 67.
Elder JS. Disorders and anomalies of the scrotal contents. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 560.
Rajpert-De Meyts E, Main KM, Toppari J, Skakkebaek NE. Testicular dysgenesis syndrome, cryptorchidism, hypospadias, and testicular tumors. In: Jameson JL, De Groot LJ, de Kretser DM, et al, eds. Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 137.
