Microwaving baby food releases burst of microplastics
When baby food comes out of the microwave, it sometimes has a little something extra than when it went in … huge numbers of microplastics that are released when the food and container heat...
Update your location to show providers, locations, and services closest to you.
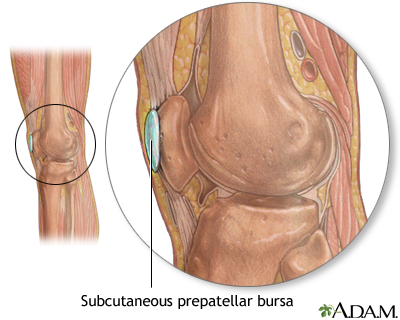
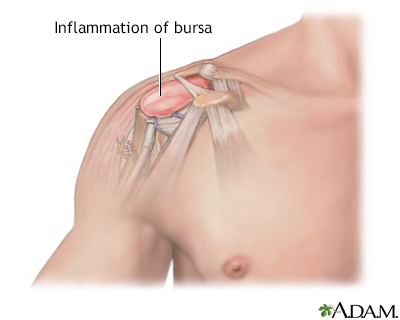
Bursitis is the swelling and irritation of a bursa. A bursa is a fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion between muscles, tendons, and bones.
Student's elbow; Olecranon bursitis; Housemaid's knee; Prepatellar bursitis; Weaver's bottom; Ischial gluteal bursitis; Baker's cyst; Gastrocnemius - semimembranosus bursa
Bursitis is often a result of overuse. It can also be caused by a change in activity level, such as training for a marathon, or by being overweight.
Other causes include trauma, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or infection. Sometimes, the cause can't be found.
Bursitis commonly occurs in the shoulder, knee, elbow, and hip. Other areas that may be affected include the area around the Achilles tendon and the foot.
Symptoms of bursitis may include any of the following:
The health care provider will ask about your medical history and perform a physical exam.
Tests that may be ordered include:
Your provider will talk to you about a treatment plan to help you resume your normal activities, including some of the following tips.
Tips to relieve bursitis pain:
For bursitis around the hips, knees, or ankle:
You should avoid activities that involve repetitive movements of any body part when possible.
Other treatments include:
As the pain goes away, your provider may suggest exercises to build strength and keep movement in the painful area.
In rare cases, surgery is done.
Some people do well with treatment. When the cause cannot be corrected, you may have long-term pain.
If the bursa is infected, it becomes more inflamed and painful. This often requires antibiotics or surgery.
Contact your provider if symptoms recur or do not improve after 3 to 4 weeks of treatment, or if the pain is getting worse.
When possible, avoid activities that include repetitive movements of any body parts. Be aware of your posture when doing the activities. Strengthening your muscles and working on your balance may help decrease the risk of bursitis.

Biundo JJ. Bursitis, tendinitis, and other periarticular disorders and sports medicine. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 247.
Hogrefe C, Jones EM. Tendinopathy and bursitis. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, Erickson TB, Wilcox SR, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 103.

When baby food comes out of the microwave, it sometimes has a little something extra than when it went in … huge numbers of microplastics that are released when the food and container heat...