Definition
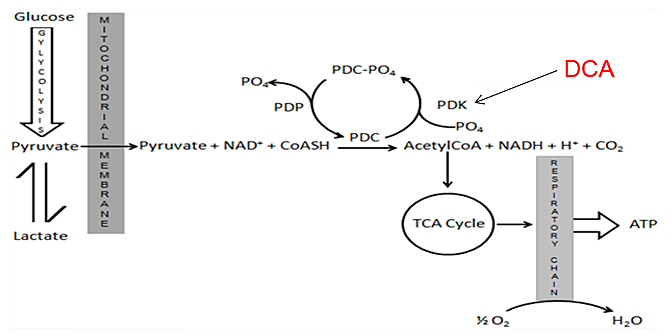
Lactic acidosis refers to lactic acid build up in the bloodstream. Lactic acid is produced when oxygen levels become low in cells within the areas of the body where metabolism takes place.
Causes
The most common cause of lactic acidosis is severe medical illness in which blood pressure is low and too little oxygen is reaching the body's tissues. Intense exercise or convulsions can cause temporary lactic acidosis. Certain diseases can also cause the condition, including:
Some medicines can rarely cause lactic acidosis:
- Beta adrenergic agonist inhalers used to treat asthma or COPD (albuterol and salmeterol)
- Epinephrine
- Linezolid
- Metformin, used to treat diabetes (most often when overdosed)
- Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors used to treat HIV infection
- Propofol
Exams and Tests
Tests may include a blood test to check lactate and electrolyte levels.
Treatment
The main treatment for lactic acidosis is to correct the medical problem that causes the condition.
References
Palmer BF. Metabolic acidosis. In: Feehally J, Floege J, Tonelli M, Johnson RJ, eds. Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 12.
Seifter JL. Acid-base disorders.In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 110.
Strayer RJ. Acid-base disorders. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, et al, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 116.