Definition
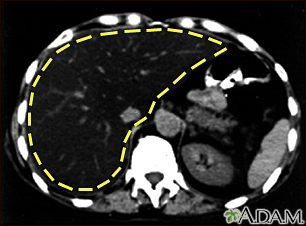
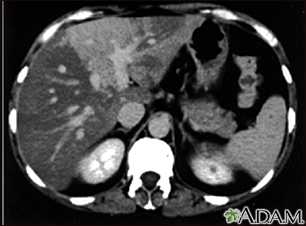
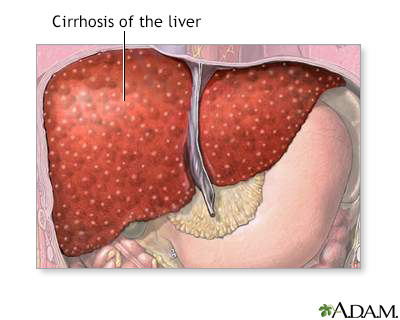
The term "liver disease" applies to many conditions that stop the liver from working or prevent it from functioning well. Abdominal pain or swelling, yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice), or abnormal results of liver function tests may suggest you have liver disease.
Related topics include:
References
Martin P. Approach to the patient with liver disease. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 137.
Williams MJ, Gordon-Walker TT. Hepatology. In: Penman ID, Ralston SH, Strachan MWJ, Hobson RP, eds. Davidson's Principles and Practice of Medicine. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 24.